Layout and Functionality of Pole Barn Homes
Pole barn house design plans – Pole barn homes offer a unique blend of rustic charm and modern functionality. Their adaptable nature allows for creative design solutions, catering to diverse family needs and lifestyles. The open floor plans often associated with pole barns present both opportunities and challenges, requiring careful consideration of layout and space optimization. This section explores three distinct floor plan examples and delves into the advantages and disadvantages of open-concept designs, as well as the strategic integration of specific rooms.
Three Pole Barn House Floor Plans for a Family of Four
The following Artikels three different floor plans, each designed to accommodate a family of four but catering to distinct preferences and lifestyle requirements. These examples demonstrate the versatility inherent in pole barn home design.
- Floor Plan 1: Open-Concept Living This plan prioritizes an expansive, interconnected living space. The kitchen, dining area, and living room flow seamlessly into one another, creating a feeling of spaciousness and promoting family interaction. A master suite with an ensuite bathroom is located on one side of the home, while two smaller bedrooms and a shared bathroom are situated on the opposite side.
A laundry room is conveniently placed near the bedrooms. This design emphasizes communal living and is ideal for families who enjoy spending time together.
- Floor Plan 2: Home Office and Workshop Integration This design incorporates a dedicated home office and a sizable workshop, reflecting the needs of a family with work-from-home professionals or hobbyists. The home office is situated near the main living area for easy access, yet separated enough to provide a quiet workspace. The large workshop, ideally located at the rear of the house, can be accessed from both the interior and exterior, maximizing its functionality.
The living area maintains an open-concept feel, while the bedrooms and bathrooms are positioned to ensure privacy.
- Floor Plan 3: Emphasis on Master Suite and Bonus Room This floor plan prioritizes the master suite, featuring a large bedroom, a spacious bathroom with a walk-in shower and soaking tub, and a walk-in closet. A bonus room, potentially used as a guest room, home gym, or playroom, is located near the bedrooms but separated from the main living area. The kitchen, dining, and living areas maintain an open-concept layout, while the remaining bedrooms and a shared bathroom are positioned for privacy.
This design caters to families who value a luxurious master retreat and a flexible additional space.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Open-Concept Designs in Pole Barn Homes
Open-concept designs are frequently featured in pole barn homes due to their ability to maximize the sense of space. However, there are both benefits and drawbacks to consider.
- Advantages: Open floor plans create a feeling of spaciousness, particularly beneficial in pole barns which often boast high ceilings. This design promotes interaction among family members and is ideal for entertaining. Natural light can easily flow throughout the entire living area.
- Disadvantages: Noise can easily carry throughout the entire space, potentially disrupting work or sleep. Privacy can be limited, and it may be challenging to define distinct zones for different activities. The lack of defined walls can make it harder to decorate and furnish effectively, requiring careful planning.
Maximizing space and functionality in an open-concept layout requires strategic furniture placement and the use of room dividers or area rugs to delineate distinct zones. Built-in shelving and cabinetry can provide ample storage while maintaining a clean aesthetic.
Incorporation of Specific Rooms into Pole Barn House Designs
Strategic placement of specific rooms is crucial for maximizing functionality in a pole barn home.
Pole barn house design plans offer a versatile and cost-effective approach to home building, particularly appealing for those seeking open floor plans and customizable spaces. For those desiring a waterfront property, consider the aesthetic appeal of lake house home design plans which often incorporate similar principles of open layouts and natural light. However, the robust and durable construction of pole barns makes them equally suitable for various climates and terrains, making them a strong contender even beyond lakeside locations.
- Master Suite: Ideally located away from the main living area for privacy, often including an ensuite bathroom and walk-in closet.
- Mudroom: A practical addition near the main entrance to store coats, shoes, and outdoor gear, keeping the main living areas clean.
- Bonus Room: Versatile space that can be adapted to suit various needs; its placement can be flexible, depending on the overall design and family preferences.
Building Materials and Costs
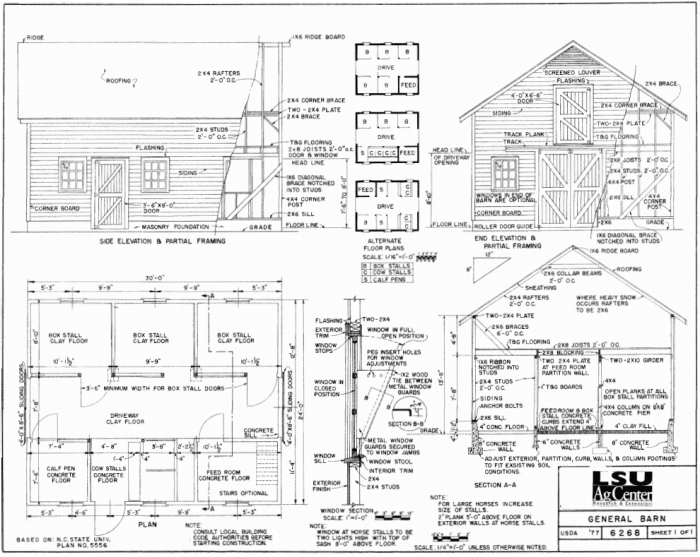
Constructing a pole barn home offers a unique blend of affordability and customization, but material choices significantly impact both the initial investment and long-term maintenance. Understanding the cost-effectiveness of different materials is crucial for budgeting and ensuring a durable, energy-efficient structure.
Material Cost Comparison
Choosing the right building materials is a critical decision affecting both the initial cost and the long-term performance of your pole barn home. The following table compares common materials based on cost, durability, and maintenance needs. Note that prices are estimates and can vary based on location, supplier, and quality.
| Material | Estimated Cost per Square Foot | Durability | Maintenance Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal Siding | $5-$15 | High; resistant to rot, insects, and fire | Low; occasional cleaning and touch-ups |
| Wood Siding (e.g., LP SmartSide) | $6-$12 | Moderate to High; durable with proper treatment | Moderate; periodic painting or staining, potential for rot or insect damage if not treated |
| Concrete (for walls or foundation) | $8-$20 | Very High; extremely durable and long-lasting | Low; minimal maintenance required |
| Vinyl Siding | $4-$10 | Moderate; relatively durable but susceptible to damage | Low; easy to clean |
Insulation Options for Pole Barn Homes
Proper insulation is essential for energy efficiency and comfort in a pole barn home, especially in climates with extreme temperatures. Several options exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages concerning cost and effectiveness.
Common insulation choices include fiberglass batts, spray foam, and cellulose. Fiberglass batts are relatively inexpensive and easy to install, but may not provide the same level of air sealing as spray foam. Spray foam offers superior insulation and air sealing capabilities, leading to lower energy bills, but is more expensive to install. Cellulose insulation is a cost-effective and environmentally friendly option, offering good insulation value.
The best choice depends on your budget and desired level of energy efficiency.
Estimated Construction Costs for a 1500 sq ft Pole Barn House, Pole barn house design plans
The total cost of constructing a 1500 sq ft pole barn house varies considerably depending on location, finishes, and labor costs. However, a reasonable estimate can be provided to illustrate the potential expense.
Assuming a mid-range construction approach using metal siding, wood framing, and fiberglass insulation, the estimated breakdown might look like this:
| Cost Category | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Site preparation and foundation | $10,000 – $20,000 |
| Framing and sheathing | $20,000 – $30,000 |
| Exterior finishes (siding, roofing) | $15,000 – $25,000 |
| Interior finishes (drywall, flooring, fixtures) | $25,000 – $40,000 |
| Insulation and HVAC | $10,000 – $15,000 |
| Labor (including permits and inspections) | $30,000 – $50,000 |
| Total Estimated Cost | $110,000 – $190,000 |
This is a broad estimate, and actual costs can vary significantly. Factors such as the complexity of the design, the cost of land, and the availability of skilled labor will all affect the final price. It is crucial to obtain multiple bids from contractors to get a more accurate cost estimate for your specific project.
Environmental Considerations
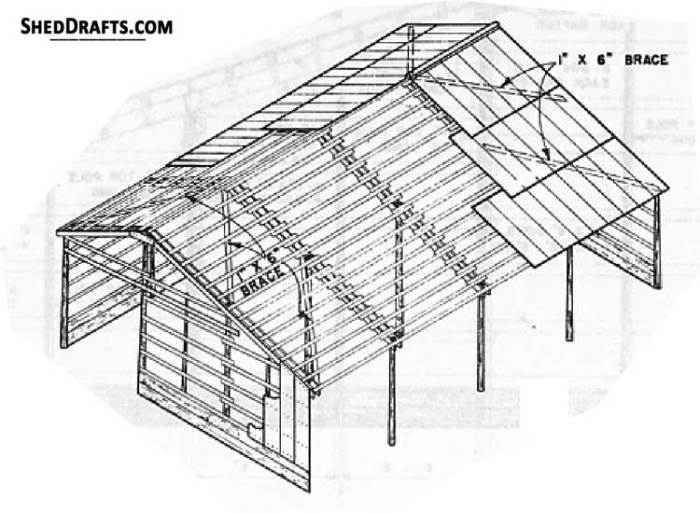
Building a pole barn home presents a unique opportunity to minimize environmental impact, but careful consideration of material sourcing and construction practices is crucial. The overall environmental footprint depends significantly on the choices made throughout the design and building process. Sustainable practices can significantly reduce the negative effects, creating a home that is both affordable and environmentally responsible.The environmental impact of a pole barn house stems primarily from the materials used in its construction and the energy consumed during its lifespan.
The sourcing of lumber, for example, can have a considerable effect. Choosing sustainably harvested wood from certified forests significantly reduces the contribution to deforestation and habitat loss. Similarly, the use of recycled or reclaimed materials in various aspects of the build, from the framing to the insulation, can drastically lessen the demand for newly manufactured products, lowering the overall carbon footprint.
Energy consumption, encompassing heating, cooling, and lighting, is another key factor; employing energy-efficient technologies and design strategies helps mitigate this impact.
Material Sourcing and its Environmental Impact
The selection of building materials directly influences the environmental footprint of a pole barn home. Sourcing lumber from responsibly managed forests, certified by organizations like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), ensures that wood is harvested in a way that minimizes damage to ecosystems. Using reclaimed or recycled materials, such as repurposed wood beams or recycled steel for roofing, reduces the demand for new resources and lowers embodied carbon.
Consideration should also be given to the transportation distances of materials; choosing locally sourced materials reduces fuel consumption associated with transportation. For example, using locally-quarried stone for foundation elements minimizes the environmental impact of long-distance shipping.
Sustainable Building Practices
Integrating sustainable building practices into the design and construction of a pole barn home is key to minimizing its environmental impact. This includes employing energy-efficient design strategies such as proper insulation, high-performance windows, and strategic placement to maximize natural light and minimize heating and cooling loads. Passive solar design, for instance, can significantly reduce reliance on energy-intensive heating and cooling systems.
The use of locally sourced, sustainably harvested materials, as previously mentioned, is another crucial aspect. Furthermore, incorporating rainwater harvesting systems for irrigation or toilet flushing can reduce water consumption, contributing to overall sustainability. Finally, selecting low-VOC (volatile organic compound) paints and finishes reduces indoor air pollution.
Minimizing Environmental Footprint Through Design Choices
Several design choices can minimize the environmental footprint of a pole barn home. The incorporation of energy-efficient features, such as solar panels for electricity generation or geothermal heating and cooling systems, significantly reduces reliance on fossil fuels. Employing high-performance insulation, including spray foam or dense-packed cellulose, minimizes energy loss through the building envelope. Designing for natural ventilation can reduce the need for air conditioning, further decreasing energy consumption.
The use of recycled or reclaimed materials, as previously highlighted, is a crucial strategy. Examples include using recycled metal roofing, reclaimed lumber for interior finishes, or recycled plastic lumber for decking. These choices reduce the demand for new resources and decrease waste sent to landfills.
Permits and Regulations: Pole Barn House Design Plans
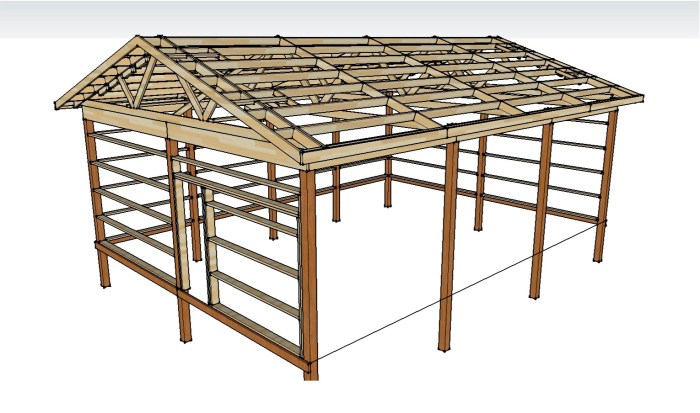
Constructing a pole barn house, even in a suburban setting, necessitates navigating a complex web of permits and regulations. Understanding these requirements upfront is crucial for a smooth and timely building process, preventing costly delays and potential legal issues. Failure to obtain the necessary approvals can lead to stop-work orders, fines, and even the demolition of partially or fully completed structures.Securing the necessary permits involves a multi-step process that requires careful planning and communication with local authorities.
The specific requirements vary significantly depending on location, with some jurisdictions having stricter regulations than others. This section will Artikel common permit types and potential challenges, offering strategies for navigating the process successfully.
Necessary Permits and Regulations
The permits required for a pole barn house project typically include, but are not limited to, building permits, electrical permits, plumbing permits, and septic permits (if applicable). Building permits are usually the most comprehensive, encompassing structural aspects, foundation requirements, and adherence to building codes. Electrical and plumbing permits ensure that these systems meet safety standards and are properly installed.
Septic permits, necessary for properties without access to municipal sewer systems, govern the design and installation of septic tanks and leach fields. Zoning regulations, which dictate land use and building restrictions within a specific area, must also be considered. For example, setback requirements, which define the minimum distance a structure must be from property lines, are frequently a significant factor in pole barn house designs.
Height restrictions and limitations on building size are other common zoning considerations. These regulations vary widely; a rural area might have far less stringent rules than a densely populated suburb.
Potential Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Obtaining permits for pole barn homes can present unique challenges. Some jurisdictions may have limited experience with pole barn construction, leading to misunderstandings or delays in the approval process. The unconventional nature of pole barn houses compared to traditional stick-built homes might require additional documentation or clarification. Another potential challenge lies in demonstrating compliance with building codes, especially regarding structural integrity and energy efficiency.
A common strategy to overcome these challenges is to work closely with a qualified architect or engineer familiar with pole barn construction. They can provide detailed plans and specifications that clearly address the concerns of building inspectors and zoning officials. Proactive communication with the local authorities, including early consultations and providing comprehensive documentation, is also vital. This can help to identify and address potential issues before they become major obstacles.
In some cases, seeking a variance or exception to specific regulations may be necessary if the design doesn’t perfectly meet existing codes. This process usually involves a formal application and a hearing before the relevant planning board.
Working with Local Authorities
Successful navigation of the permit process hinges on effective communication and collaboration with local authorities. This begins with thorough research to understand the specific requirements of the jurisdiction. It’s crucial to review zoning ordinances, building codes, and any other relevant regulations before finalizing the design plans. The submission of complete and accurate applications, along with all necessary supporting documentation, is essential for expediting the review process.
This documentation may include architectural plans, engineering calculations, and materials specifications. Maintaining open communication with the building inspector throughout the construction process is also highly recommended. This allows for prompt clarification of any questions or concerns and helps prevent unforeseen delays or conflicts. Regular inspections by the building inspector are a standard part of the process, and timely completion of these inspections is essential for maintaining progress.
If challenges arise during the inspection process, it’s crucial to address them proactively and collaboratively with the inspector to find mutually agreeable solutions. Patience and persistence are key attributes in working successfully with local authorities.
Top FAQs
What is the average lifespan of a pole barn house?
With proper maintenance, a well-constructed pole barn house can last 50 years or more.
Are pole barn houses energy-efficient?
Yes, with proper insulation and energy-efficient windows and appliances, pole barns can be very energy-efficient.
Can I finance a pole barn house construction?
Yes, many lenders offer financing options for pole barn house construction. Check with your bank or credit union.
What type of foundation is used for pole barn houses?
Pole barn houses typically utilize a pier and beam foundation, or sometimes concrete slabs.
Are there any restrictions on the size of a pole barn house?
Yes, local zoning regulations will dictate size limits and other restrictions. Check with your local authorities.



