Introduction to African House Design Styles: African House Design Plans

African house design plans – African architecture boasts an incredible diversity, reflecting the continent’s vast array of cultures, climates, and available resources. The designs are not monolithic; instead, they showcase a rich tapestry of styles shaped by centuries of tradition, innovation, and adaptation to the environment. Understanding these styles requires acknowledging the interplay of historical influences, from indigenous building techniques to the impact of colonialism and globalization.
Historical and Cultural Influences on African House Design
The architectural styles across Africa are deeply rooted in the historical and cultural contexts of their respective regions. Indigenous knowledge and practices, passed down through generations, formed the foundation of many traditional building methods. Materials readily available in each area—such as mud, thatch, timber, and stone—dictated construction techniques and aesthetic choices. For instance, the availability of clay led to the development of sophisticated mud-brick construction in many parts of West Africa, while the abundance of timber in central Africa influenced the construction of elaborate timber-framed structures.
The influence of trade routes and interactions between different cultures also played a significant role, leading to the exchange of ideas and techniques, resulting in hybrid architectural forms. Later, colonial influences introduced new materials and building styles, often leading to a blend of traditional and modern approaches.
Prominent Architectural Features in Various African Regions, African house design plans
Several architectural features are commonly found across various regions, though their specific forms and interpretations vary considerably. Many traditional African houses prioritize natural ventilation and shade, employing features like high ceilings, overhanging eaves, and strategically placed windows to mitigate harsh climates. Courtyards, often found in North and West African architecture, provide shaded outdoor spaces for social interaction and domestic activities.
The use of decorative elements, such as intricate carvings, painted murals, and geometric patterns, is prevalent in many styles, serving both aesthetic and symbolic purposes. The integration of vernacular architecture with modern techniques has also led to innovative designs that preserve cultural heritage while adapting to contemporary needs.
Comparison of African House Design Styles
The following table compares and contrasts four distinct African house design styles, highlighting their unique characteristics:
| Style Name | Region | Key Features | Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Round Hut (Kraal) | Southern Africa | Circular structure, thatched roof, often clustered in villages | Mud, thatch, timber |
| Compound House | West Africa | Multiple buildings arranged around a central courtyard, often multi-story | Mud brick, thatch, timber |
| Maasai Manyatta | East Africa | Temporary, portable structures made of sticks and animal skins | Wood, animal skins, thatch |
| Adobe Architecture | North Africa | Rectangular structures, flat roofs, thick walls for insulation | Sun-dried mud bricks (adobe), timber, plaster |
Modern Interpretations of African House Designs
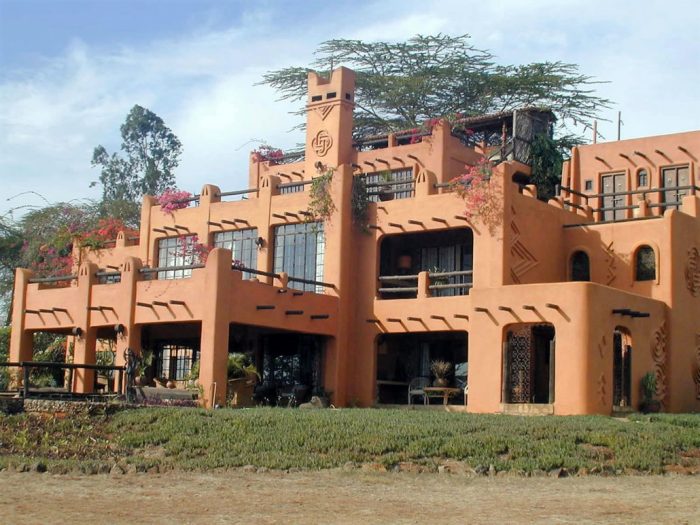

Modern African architecture represents a fascinating fusion of time-honored traditions and contemporary design sensibilities. It’s a dynamic movement that respects heritage while embracing innovative techniques and sustainable practices. This blend creates homes that are both aesthetically pleasing and environmentally responsible, reflecting a unique cultural identity within a global context.The integration of traditional African aesthetics with contemporary architectural trends is evident in the use of local materials, such as thatch, timber, and rammed earth, alongside modern building technologies like solar panels and energy-efficient windows.
This approach not only preserves cultural heritage but also reduces the environmental impact of construction and ongoing operation. Furthermore, the incorporation of traditional design elements, such as vibrant colors, intricate patterns, and open-plan layouts, creates a sense of place and connection to the rich history of African design.
African house design plans often prioritize functionality and blend seamlessly with the surrounding environment. The concept of integrating natural materials and open-air spaces is quite common, a stark contrast to some more unusual structures, such as those found in a strange design public house , which often prioritize bold aesthetics. However, even these unconventional designs can offer inspiration for unique elements within African architectural styles, prompting innovative solutions in home planning.
Examples of Modern Houses Incorporating Traditional African Design Elements
Modern African homes often seamlessly blend traditional elements with contemporary styles. For instance, a house might feature a thatched roof, a classic African element, atop a sleek, modern concrete structure. Intricate carvings, reminiscent of traditional tribal art, can adorn the walls or window frames, while large, open windows allow for natural light and ventilation, a common feature in traditional African homes designed to adapt to the climate.
The use of earth tones and vibrant colors in the exterior and interior palettes further enhances the connection to the continent’s rich visual heritage.
Sustainable Design Principles in Modern African Homes
Sustainable design is increasingly central to modern African architecture. Many homes are built using locally sourced, sustainable materials to minimize transportation costs and carbon emissions. Passive design strategies, such as maximizing natural light and ventilation, are employed to reduce reliance on artificial heating and cooling. Solar panels are commonly integrated into the roof design, providing a renewable energy source.
Water harvesting systems collect rainwater for non-potable uses, minimizing water consumption. Furthermore, the incorporation of green spaces and landscaping contributes to a healthier and more sustainable living environment.
Three Modern African House Design Examples
Design 1: The Coastal Retreat This design emphasizes natural light and ventilation. Imagine a single-story house with a high, pitched thatched roof, wide verandas offering shade, and large windows facing the ocean breeze. The walls are constructed from locally sourced timber, treated for durability. Solar panels are discreetly integrated into the roofline. The interior uses light, natural materials and incorporates vibrant colors inspired by the surrounding landscape.
Design 2: The Inland Oasis This design prioritizes energy efficiency and water conservation. Picture a two-story house built using rammed earth, a naturally insulating material. The walls are thick, reducing the need for extensive climate control. A courtyard at the center of the house provides natural ventilation and shade. A rainwater harvesting system collects and stores water for non-potable use, supplementing the main water supply.
The design incorporates traditional geometric patterns in the exterior facade.
Design 3: The Urban Villa This design blends modern aesthetics with traditional craftsmanship. Imagine a three-story house with a contemporary concrete frame, accented by intricate wood carvings inspired by local tribal art. The interior is open-plan, with large windows offering city views. Sustainable features include energy-efficient appliances and a green roof, reducing the urban heat island effect. The color palette features earthy tones contrasted with pops of vibrant color inspired by traditional textiles.
Challenges and Opportunities in African House Design

Providing affordable and sustainable housing across the diverse landscapes and socio-economic contexts of Africa presents a significant challenge. The complexities of rapid urbanization, climate change impacts, and fluctuating economic conditions all contribute to a housing crisis impacting millions. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovative and sustainable development, particularly when leveraging traditional building techniques and integrating modern technologies.
Challenges in Affordable and Sustainable Housing
The primary obstacles to affordable and sustainable housing in Africa include limited access to finance, inadequate infrastructure (particularly reliable water and sanitation), a shortage of skilled labor, and the high cost of building materials. Furthermore, environmental concerns such as deforestation and the depletion of natural resources necessitate sustainable building practices. The lack of consistent building codes and regulations across different regions also contributes to the problem, leading to inconsistencies in quality and safety.
Rapid urbanization in many African cities exacerbates these issues, placing immense pressure on existing resources and infrastructure.
Opportunities for Innovation and Sustainable Development
The need for affordable and sustainable housing creates a fertile ground for innovation. Locally sourced materials, such as earth bricks, bamboo, and recycled materials, offer cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional construction methods. Innovative design approaches, incorporating passive cooling techniques and natural ventilation, can reduce energy consumption and reliance on costly air conditioning. Furthermore, exploring modular and prefabricated construction methods can streamline the building process and reduce construction time and labor costs.
The potential for creating green jobs through sustainable building practices is also a significant opportunity.
The Role of Technology and Collaboration
Technology plays a crucial role in overcoming the challenges of affordable and sustainable housing. Computer-aided design (CAD) software enables efficient design and planning, while 3D printing technology offers the potential for rapid and cost-effective construction of housing units. Building Information Modeling (BIM) can improve collaboration and coordination among stakeholders throughout the construction process. Furthermore, the use of mobile technology can facilitate access to information, training, and financial services for builders and homeowners.
Successful implementation requires strong collaboration between governments, private sector companies, NGOs, and local communities.
Examples of Successful Community-Based Housing Projects
Several community-based housing projects across Africa demonstrate the successful integration of traditional and modern design elements. For example, the use of locally sourced materials combined with modern energy-efficient technologies has resulted in affordable and sustainable housing solutions in rural communities in Kenya. In South Africa, initiatives promoting participatory design processes have empowered communities to build homes that reflect their cultural preferences and environmental needs.
These projects highlight the importance of community involvement and culturally sensitive design in achieving successful outcomes. One such project, focusing on using compressed earth blocks (CEB) in rural Senegal, resulted in a significant reduction in housing costs while simultaneously improving the thermal performance of the dwellings. This project also successfully integrated local building techniques with modern design principles.
Questions Often Asked
What are the common challenges in designing affordable housing in Africa?
Challenges include limited access to resources, fluctuating material costs, inadequate infrastructure, and the need to balance affordability with sustainability and resilience to extreme weather conditions.
How do traditional African building methods contribute to sustainability?
Traditional methods often utilize locally sourced, readily available materials, minimizing transportation costs and environmental impact. Passive design strategies like natural ventilation and shading further enhance energy efficiency.
What role does technology play in modern African house design?
Technology assists in optimizing designs for energy efficiency, utilizing sustainable materials effectively, and facilitating collaboration amongst architects, engineers, and communities to develop innovative and affordable solutions.
Are there any examples of successful community-based housing projects in Africa?
Many successful projects integrate traditional building techniques with modern materials and sustainable principles, often involving community participation in design and construction to ensure cultural relevance and affordability.