Steel Frame House Design

Steel frame house design – Steel frame houses are gaining popularity as a modern alternative to traditional wood-framed homes. This construction method offers a unique blend of advantages and disadvantages that prospective homeowners should carefully consider before making a decision. Understanding these aspects is crucial for informed decision-making in residential construction.
Steel Frame House Design: Advantages
The use of steel in residential construction offers several compelling advantages. Steel’s inherent strength allows for larger spans between supporting walls, resulting in more open floor plans and greater design flexibility. This is particularly beneficial for contemporary architectural styles that prioritize spacious interiors. Furthermore, steel is remarkably resistant to pests, rot, and fire, significantly reducing maintenance and improving the overall longevity of the structure.
Its lightweight nature simplifies transportation and handling during construction, potentially leading to faster build times and reduced labor costs. Finally, steel’s inherent durability contributes to a longer lifespan compared to wood, potentially increasing the home’s resale value. Pre-fabricated steel components also enhance precision and minimize on-site waste, promoting sustainable building practices.
Steel Frame House Design: Disadvantages
Despite its benefits, steel frame construction presents some challenges. Steel’s susceptibility to corrosion is a significant concern, necessitating proper surface treatment and protective coatings. This adds to the initial construction cost. The thermal conductivity of steel means that adequate insulation is crucial to prevent energy loss and maintain comfortable indoor temperatures. Improper installation can lead to thermal bridging, reducing the effectiveness of insulation.
Steel frame house design offers a contemporary approach to construction, known for its strength and efficiency. However, the aesthetic possibilities are vast; you can achieve a charming rustic look, similar to the elegance found in french country house design , by carefully selecting exterior materials and detailing. Ultimately, the versatility of steel framing allows for a wide range of architectural styles, including those inspired by classic European designs.
Furthermore, the specialized skills required for steel frame construction may limit the availability of contractors, potentially increasing labor costs. Finally, the potential for noise transmission through steel framing necessitates careful attention to soundproofing during the construction process.
Steel Frame House Design: Lifespan and Maintenance
Steel frame houses, when properly constructed and maintained, boast a significantly longer lifespan than wood-framed homes. While wood is susceptible to rot, insect infestation, and fire damage, steel’s inherent resistance to these factors contributes to its extended durability. However, regular maintenance is still essential to address potential corrosion and ensure the structural integrity of the building. This involves periodic inspections for signs of rust or damage, along with appropriate repainting or recoating as needed.
Compared to the regular maintenance and potential repairs associated with wood-framed houses (such as termite treatment or replacing rotted sections), the maintenance requirements for steel frames are generally less frequent and less extensive.
Steel Frame House Design: Examples of Framing Systems
Understanding the various steel framing systems used in residential construction is crucial for informed decision-making. Different systems offer varying advantages and disadvantages based on factors like cost, complexity, and structural performance.
| System Name | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light Gauge Steel Framing (LGS) | Uses thin, cold-formed steel sections for walls, floors, and roofs. | Cost-effective, lightweight, precise, fast construction, and excellent dimensional stability. | Susceptible to corrosion if not properly protected, requires specialized tools and expertise. |
| Heavy Gauge Steel Framing | Employs thicker steel sections for greater load-bearing capacity, typically used in taller or more complex structures. | High strength and durability, suitable for large spans and heavy loads. | Higher cost, more challenging to install, requires specialized equipment and expertise. |
| Steel Stud Framing | Similar to LGS but utilizes steel studs as primary structural members. | Offers greater design flexibility compared to traditional wood framing. | Requires careful attention to connections and bracing to ensure stability. |
| Prefabricated Steel Modules | Entire sections of the house are pre-fabricated in a factory and assembled on-site. | Faster construction times, reduced on-site labor, improved quality control. | Requires careful planning and coordination, potential transportation challenges for larger modules. |
Design Considerations for Steel Frame Houses
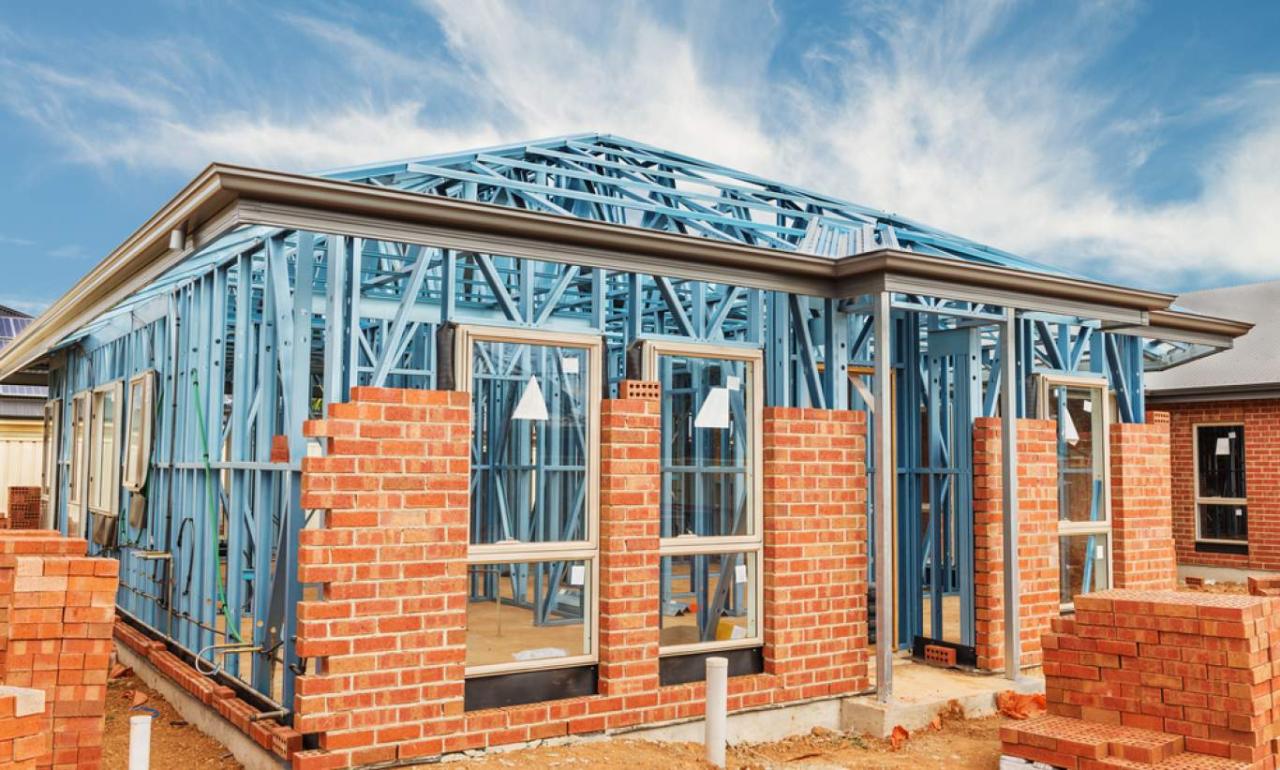

Steel frame construction offers numerous advantages, including speed of construction, design flexibility, and resilience. However, careful consideration of several key design aspects is crucial to ensure the structural integrity, energy efficiency, and longevity of the building. This section will delve into critical design considerations specific to steel frame houses.
Seismic Activity and Steel Frame Design
Seismic activity presents a significant challenge in many regions. Steel’s inherent ductility and strength make it a relatively suitable material for seismic zones, but careful engineering is paramount. Design considerations include the use of moment-resisting frames, shear walls, and bracing systems to dissipate seismic energy and prevent structural collapse. The specific design will depend on the anticipated seismic activity level, as defined by local building codes and geological surveys.
For example, a building in a high-seismic zone will require a more robust bracing system than one in a low-seismic zone. Proper connection detailing between steel members is also crucial for ensuring the structural integrity under seismic loading. Expert structural engineering is essential to ensure compliance with relevant building codes and safety standards.
Insulation and Thermal Bridging in Steel Frame Homes
Steel is a highly conductive material, meaning it readily transfers heat. This necessitates careful consideration of insulation strategies to minimize energy loss and maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. Continuous insulation is vital to minimize thermal bridging – the transfer of heat through the steel framing members. This can be achieved through the use of high-performance insulation materials installed both within the wall cavities and on the exterior of the steel framing.
Proper sealing of air gaps and penetrations is also crucial to prevent thermal bridging. The selection of insulation materials should consider their thermal performance (R-value), moisture resistance, and environmental impact. For example, spray foam insulation offers excellent thermal performance and air sealing capabilities, while mineral wool provides good thermal performance and fire resistance.
Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Features
Incorporating sustainable and energy-efficient features is increasingly important in modern construction. Steel frame construction offers opportunities to achieve this through various strategies. These include the use of high-performance windows and doors to minimize heat transfer, the installation of renewable energy systems such as solar panels, and the implementation of efficient HVAC systems. Careful orientation of the building to maximize solar gain in winter and minimize it in summer is also crucial.
Using recycled steel in the construction process reduces the environmental impact of the project. The selection of sustainable building materials for the interior finishes, such as reclaimed wood or bamboo flooring, further enhances the building’s sustainability credentials. Implementing smart home technologies for energy monitoring and control can further improve energy efficiency.
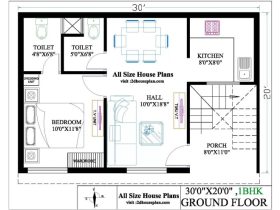
Floor Plan for a 2000 sq ft Steel Frame House
A well-designed floor plan maximizes space utilization and functionality. The following is a possible floor plan for a 2000 sq ft steel frame house with three bedrooms and two bathrooms:
- Master Bedroom: 15′ x 18′ (including ensuite bathroom)
- Ensuite Bathroom: 8′ x 10′ (shower, toilet, vanity)
- Bedroom 2: 12′ x 12′
- Bedroom 3: 12′ x 12′
- Bathroom 2: 6′ x 8′ (bathtub, toilet, vanity)
- Living Room: 18′ x 20′
- Kitchen: 14′ x 14′
- Dining Area: 12′ x 12′
- Hallway: Variable width, connecting all rooms
- Laundry Room: 6′ x 8′
- Garage (optional): 16′ x 20′ (accessible from the house)
This layout is merely a suggestion, and the actual dimensions and arrangement of rooms can be customized based on individual preferences and site conditions. The design should consider factors such as natural light, ventilation, and ease of movement between rooms.
Cost Analysis and Budgeting for Steel Frame Houses
Building a steel frame house presents a unique cost profile compared to traditional methods. Understanding this cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and project management. This section details the various cost components, influential factors, and provides a sample budget breakdown to illustrate the financial aspects of steel frame construction.
Comparison of Steel Frame House Costs with Other Construction Methods
Steel frame construction often offers competitive pricing, although the final cost depends significantly on several variables. Compared to traditional wood-frame houses, steel can sometimes be more expensive initially due to higher material costs, but it can lead to savings in labor costs due to faster construction times and potentially lower maintenance costs over the long term. Concrete construction, on the other hand, generally presents a higher initial cost than both steel and wood frame houses, but it offers superior durability and fire resistance.
The overall cost-effectiveness of each method is highly dependent on location, labor rates, and specific project requirements.
Major Cost Components in Steel Frame House Construction, Steel frame house design
The major cost components of a steel frame house project can be broadly categorized into materials, labor, and permits. Materials include the steel framing itself, roofing materials, insulation, exterior cladding, interior finishes, and any specialized components. Labor costs encompass the skilled labor required for steel erection, framing, electrical, plumbing, HVAC installation, and finishing work. Permitting fees vary by location and project complexity, including building permits, foundation permits, and inspections.
Contingency funds are also a crucial component to account for unforeseen expenses and potential price fluctuations.
Factors Influencing the Final Cost of a Steel Frame House Project
Several factors significantly impact the final cost. These include the size and complexity of the house design, the chosen materials and finishes (e.g., high-end fixtures versus standard options), the location of the project (labor and material costs vary regionally), the prevailing market conditions (fluctuations in material prices and labor rates), and the level of customization. Site preparation, foundation type, and the inclusion of specialized features (e.g., smart home technology) also contribute to the overall cost.
The experience and reputation of the builder also play a vital role; a more experienced and reputable builder may command higher fees but often delivers better quality and project management.
Sample Budget Breakdown for a Steel Frame House Project
The following table provides a sample budget breakdown for a 2,000 square foot steel frame house project. It is crucial to remember that these are estimates, and actual costs can vary depending on the factors mentioned above. This budget assumes a mid-range finish level.
| Category | Description | Estimated Cost | Percentage of Total Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Steel framing, roofing, insulation, cladding, windows, doors, interior finishes | $150,000 | 40% |
| Labor | Framing, electrical, plumbing, HVAC, finishing, site preparation | $100,000 | 27% |
| Permits and Inspections | Building permits, foundation permits, inspections | $10,000 | 3% |
| Foundation | Concrete slab or other foundation system | $30,000 | 8% |
| Contingency | Unforeseen expenses and price fluctuations | $20,000 | 5% |
| Site Preparation | Clearing, grading, excavation | $15,000 | 4% |
| Professional Fees (Architect, Engineer) | Design and engineering services | $25,000 | 7% |
| Other Costs | Landscaping, utilities hookup | $50,000 | 13% |
| Total Estimated Cost | $370,000 | 100% |
Key Questions Answered
What is the average lifespan of a steel frame house?
Steel frame houses, with proper maintenance, can last for over 100 years, significantly longer than many wood-framed homes.
Are steel frame houses more expensive than traditional homes?
Initial material costs might be higher, but the overall cost can be comparable or even lower depending on factors like labor costs and project complexity. Long-term savings on maintenance can also offset initial costs.
How fire resistant are steel frame houses?
Steel is inherently fire-resistant, though protection of the framing from extreme heat is still necessary. Proper fireproofing measures are typically included in the design.
Can I customize the design of a steel frame house?
Absolutely. Steel framing allows for considerable design flexibility, accommodating various architectural styles and personalized preferences.